Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act
In an era where digital transactions and online presence have become ubiquitous, the protection of personal information has never been more crucial. Recognizing this need, the Texas Legislature enacted the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act, a comprehensive legal framework designed to combat the growing threat of identity theft and safeguard consumers’ personal data. This article delves into the intricacies of this Lone Star State ID fraud law, exploring its key provisions, implications, and impact on both consumers and businesses in Texas.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act
The Texas identity theft Enforcement and Protection Act, also known as the Texas personal information security act, is a robust piece of legislation aimed at preventing, detecting, and prosecuting identity theft crimes in Texas. Enacted in 2005 and subsequently amended to keep pace with evolving cyber threats, this act serves as a cornerstone of Texas’s consumer identity protection efforts.
Key Provisions of the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act
The Texan data breach notification law encompasses several critical components:
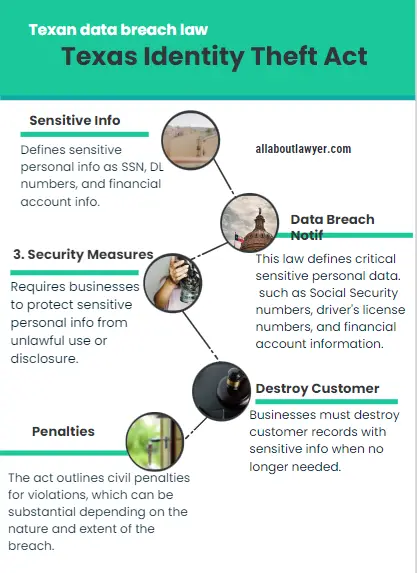
1. Definition of Sensitive Personal Information:
The act provides a clear definition of what constitutes sensitive personal information, including Social Security numbers, driver’s license numbers, and financial account information.
2. Data Breach Notification Requirements:
Organizations that experience a data breach affecting Texas residents must notify affected individuals and, in some cases, the Texas Attorney General.
3. Security Measures:
The act mandates that businesses implement reasonable procedures to protect and safeguard sensitive personal information from unlawful use or disclosure.
4. Destruction of Customer Records:
Businesses must take appropriate measures to destroy customer records containing sensitive personal information when the records are no longer needed.
5. Penalties for Non-Compliance:
The act outlines civil penalties for violations, which can be substantial depending on the nature and extent of the breach.
Read also: Is Discover Identity Theft Protection Worth It?
Data Breach Notification Protocol
One of the most significant aspects of the Texas cyber fraud prevention law is its data breach notification requirements. Under this provision:
– Entities must disclose any breach of system security to affected individuals “without unreasonable delay” and within 60 days after determining that a breach occurred.
– If a breach affects 250 or more Texas residents, the entity must also notify the Texas Attorney General within the same timeframe.
– The notification must include a description of the breach, the type of information compromised, measures taken to protect consumers, and steps individuals can take to protect themselves.
Consumer Rights and Protections
The Texas consumer identity protection framework established by this act provides several rights and protections for individuals:
1. Right to Place a Security Freeze:
Consumers have the right to place a security freeze on their credit reports, preventing new accounts from being opened in their name.
2. Access to Credit Reports:
The act ensures that consumers have access to their credit reports and can dispute inaccurate information.
3. Identity Theft Passport:
Victims of identity theft can apply for an “identity theft passport” from the Texas Attorney General’s office, which can help them restore their identity and clear fraudulent debts.
Realted Articles For You:
Identity-theft-lawyer-cost

Business Obligations and Compliance
For businesses operating in Texas, compliance with the Texan identity protection statute is critical. Key obligations include:
1. Implementing Security Measures:
Businesses must develop, implement, and maintain reasonable procedures to protect and safeguard sensitive personal information.
2. Employee Training:
Organizations should train employees on how to handle and protect sensitive personal information.
3. Data Destruction:
Proper destruction of records containing sensitive personal information when they are no longer needed for business purposes.
4. Breach Response Plan:
Developing and maintaining a comprehensive data breach response plan to ensure timely and effective action in the event of a breach.

Enforcement and Penalties
The Texas data privacy enforcement mechanisms under this act are robust:
– The Texas Attorney General has the authority to bring legal action against entities that violate the act.
– Civil penalties can range up to $50,000 per violation.
– For certain violations, penalties can increase to up to $250,000 per violation.
Impact on Cybersecurity Practices
The Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act has significantly influenced cybersecurity practices in the state:
1. Enhanced Data Protection Measures: Businesses have been compelled to invest in stronger data protection technologies and practices.
2. Increased Awareness: The act has raised awareness about the importance of data security among both businesses and consumers.
3. Standardized Breach Response: Organizations have developed more standardized and efficient data breach response procedures.
4. Cybersecurity Industry Growth: The act has indirectly contributed to the growth of the cybersecurity industry in Texas.
Challenges and Evolving Landscape
While the Texas personal information act has been largely effective, it faces ongoing challenges:
1. Technological Advancements: Rapidly evolving technology requires continuous updates to the law to address new forms of cyber threats.
2. Interstate and International Considerations: In an interconnected world, coordinating with other jurisdictions remains a challenge.
3. Small Business Compliance: Smaller businesses may struggle with the resources required for full compliance.
4. Balancing Security and User Experience: Companies must find ways to implement robust security measures without significantly impacting user experience.
Future Outlook
As cyber threats continue to evolve, the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act is likely to see further amendments and expansions:
1. AI and Machine Learning: Future updates may address the use of AI in both perpetrating and preventing identity theft.
2. Biometric Data Protection: As biometric authentication becomes more common, the act may expand to more explicitly cover this type of data.
3. IoT Device Security: With the proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices, future versions of the act may include provisions specific to these technologies.
4. Blockchain and Cryptocurrency: As these technologies become more mainstream, the act may evolve to address related identity protection concerns.
Conclusion
The Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act stands as a crucial bulwark against the rising tide of identity theft and cyber fraud. By establishing clear guidelines for data protection, breach notification, and consumer rights, this Lone Star identity misuse prevention legislation has set a strong foundation for cybersecurity practices in Texas.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the act’s effectiveness will depend on its ability to adapt to new challenges. However, its core principles of protecting personal information, enforcing data security measures, and empowering consumers remain as relevant as ever.
For businesses operating in Texas, compliance with this act is not just a legal obligation but a critical component of building trust with customers and safeguarding their reputation in an increasingly data-driven world. For consumers, understanding their rights under this act is essential for protecting their personal information and responding effectively in the event of a data breach.
As we move forward in the digital age, the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act will undoubtedly continue to play a pivotal role in shaping the cybersecurity landscape of the Lone Star State, serving as a model for similar legislation across the nation.
FAQs
Q: What is considered sensitive personal information under the Texas Identity Theft Enforcement and Protection Act?
A: Sensitive personal information includes an individual’s first name or first initial and last name in combination with their Social Security number, driver’s license number, financial account information, or certain health information.
Q: How quickly must a business notify individuals of a data breach under this act?
A: Businesses must notify affected individuals without unreasonable delay and no later than 60 days after determining that a breach occurred.
Q: Are there any exemptions to the notification requirement?
A: Yes, notification may not be required if the business determines that the breach does not create a substantial risk of harm to the affected individuals.
Q: What penalties can businesses face for violating this act?
A: Civil penalties can range up to $50,000 per violation, with the potential to increase to $250,000 for certain violations.
Q: How can consumers place a security freeze on their credit reports under this act?
A: Consumers can contact each of the three major credit reporting agencies (Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion) to request a security freeze. The act ensures that this service is provided free of charge.
About the Author

Sarah Klein, JD, is a former consumer rights attorney who spent years helping clients with issues like unfair billing, product disputes, and debt collection practices. At All About Lawyer, she simplifies consumer protection laws so readers can defend their rights and resolve problems with confidence.
Read more about Sarah
