Which Government Bodies Make Consumer Protection Laws? A Multi-Level Approach to Safeguarding Consumer Rights
In today’s complex marketplace, consumer protection laws play a crucial role in safeguarding the rights and interests of buyers. These laws are designed to ensure fair trade practices, product safety, and ethical business conduct. But have you ever wondered which government bodies make consumer protection laws regulations? This comprehensive guide will explore the various entities involved in crafting consumer protection laws at different levels of government.
Table of Contents
Federal Agencies: The Frontline of Consumer Protection
At the federal level, several agencies are tasked with creating and enforcing consumer protection laws. These bodies work to ensure a fair and safe marketplace across the entire United States.
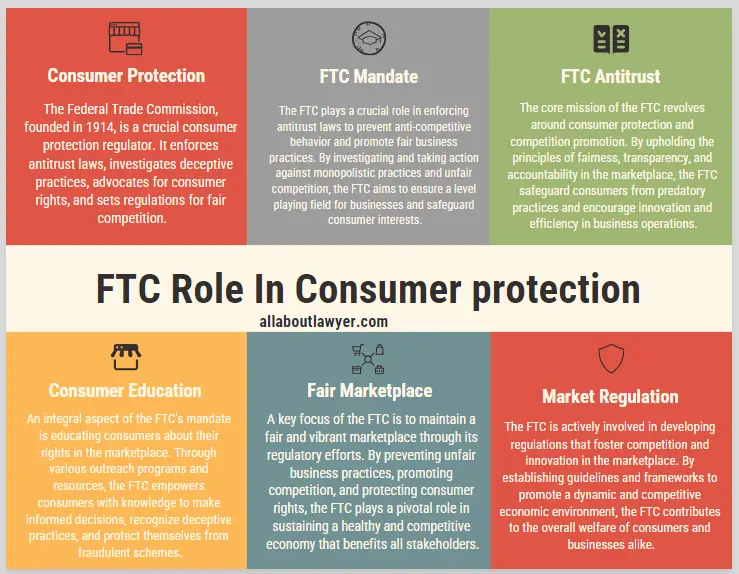
1. Federal Trade Commission (FTC)
The FTC is perhaps the most well-known consumer safeguard regulator. Established in 1914, its primary mission is to protect consumers and promote competition. The FTC’s responsibilities include:
– Enforcing antitrust laws
– Investigating and stopping unfair or deceptive business practices
– Educating consumers about their rights
– Developing rules to ensure a vibrant marketplace
2. Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB)
Created in 2011 as part of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, the CFPB focuses specifically on financial products and services. Its roles encompass:
– Regulating banks, credit unions, and other financial companies
– Enforcing federal consumer financial laws
– Restricting unfair, deceptive, or abusive practices in the financial sector
– Promoting financial education

3. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
While primarily known for its role in regulating food and drugs, the FDA also plays a significant part in consumer protection. Its consumer-focused responsibilities include:
– Ensuring the safety of food, drugs, medical devices, and cosmetics
– Regulating tobacco products
– Advancing public health through innovations that make medicines and foods more effective, safer, and affordable
4. Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC)
The CPSC is dedicated to protecting consumers from risks associated with consumer products. Its duties involve:
– Developing product safety standards
– Issuing recalls of dangerous products
– Conducting research on potential product hazards
– Informing and educating consumers about product safety

5. Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
The FCC regulates interstate and international communications by radio, television, wire, satellite, and cable. In terms of consumer protection, it:
– Enforces regulations against unwanted telephone marketing calls and robocalls
– Protects consumer privacy in communication services
– Ensures fair and reasonable rates for communication services

State-Level Consumer Protection: Closer to Home
While federal agencies provide a broad framework for consumer protection, state governments also play a crucial role in safeguarding consumer interests at a more localized level.
1. State Attorneys General Offices
Each state has an Attorney General’s office, which often includes a consumer protection division. These offices:
– Enforce state consumer protection laws
– Investigate consumer complaints
– File lawsuits against companies violating consumer rights
– Provide consumer education and resources
2. State Consumer Protection Agencies
Many states have dedicated consumer protection agencies or departments. These bodies:
– Handle consumer complaints
– Conduct investigations into unfair business practices
– Provide consumer education and outreach
– Enforce state-specific consumer protection laws
3. State Legislatures
State legislatures are responsible for creating state-specific consumer protection laws. They can:
– Pass laws that provide additional protections beyond federal regulations
– Address unique consumer issues relevant to their state
– Establish state-level consumer protection agencies
Local Government | The Grassroots of Consumer Protection
Even at the local level, there are government bodies that contribute to consumer protection efforts.
1. County and City Consumer Affairs Departments
Many counties and large cities have consumer affairs departments that:
– Handle local consumer complaints
– Provide mediation services for consumer disputes
– Offer consumer education programs
– Enforce local consumer protection ordinances
2. Local Health Departments
While primarily focused on public health, local health departments also play a role in consumer protection by:
– Inspecting restaurants and food establishments
– Enforcing local food safety regulations
– Responding to consumer complaints about health and safety issues
Collaborative Efforts in Consumer Protection
It’s important to note that these various government bodies often work together to ensure comprehensive consumer protection. For example:
– The FTC collaborates with state Attorneys General on multi-state investigations and enforcement actions.
– Federal agencies provide guidance and support to state and local consumer protection efforts.
– State and local agencies often refer cases to federal authorities when they involve interstate commerce or fall under federal jurisdiction.
The Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
While not government bodies, certain non-governmental organizations play a significant role in shaping consumer protection policies and supporting enforcement efforts.
1. Consumer Advocacy Groups
Organizations like Consumer Reports and Public Citizen:
– Conduct independent product testing and research
– Lobby for stronger consumer protection laws
– Educate consumers about their rights and product safety
2. Better Business Bureau (BBB)
The BBB, while not a government agency, works to promote marketplace trust by:
– Providing business ratings and reviews
– Mediating consumer disputes
– Reporting on marketplace trends and scams
Emerging Areas of Consumer Protection
As technology and markets evolve, new areas of consumer protection are emerging, requiring government bodies to adapt and expand their focus.
1. Digital Privacy and Cybersecurity
With the increasing prevalence of online transactions and data collection, agencies like the FTC and state Attorneys General are focusing more on:
– Protecting consumer data privacy
– Enforcing data breach notification laws
– Combating identity theft and online fraud
2. Sustainable and Ethical Consumption
Government bodies are increasingly addressing consumer protection in the context of environmental and ethical concerns:
– The FTC provides guidelines on environmental marketing claims
– State agencies are developing regulations around “green” products and sustainability claims
3. Sharing Economy and Gig Workers
As new business models emerge, consumer protection agencies are grappling with how to protect both consumers and workers in the sharing economy:
– State legislatures are passing laws to regulate ride-sharing and home-sharing services
– The CFPB is examining financial products targeted at gig workers
Conclusion
Consumer protection laws are crafted and enforced by a complex network of government bodies at the federal, state, and local levels. From the broad oversight of federal agencies like the FTC and CFPB to the localized efforts of state Attorneys General and city consumer affairs departments, these entities work together to ensure a fair and safe marketplace for all consumers.
As our economy and technology continue to evolve, so too will the landscape of consumer protection. Government bodies at all levels will need to remain vigilant and adaptable to address new challenges and protect consumer interests in an ever-changing world.
By understanding which government bodies are responsible for consumer protection, consumers can better navigate the system, know where to turn for help, and play an active role in ensuring their rights are protected in the marketplace.
FAQs
Q: Can I report a consumer protection violation to multiple government agencies?
A: Yes, you can report violations to relevant agencies at federal, state, and local levels. Each agency may have different jurisdictions and capabilities to address your complaint.
Q: Do consumer protection laws vary by state?
A: Yes, while federal laws provide a baseline, states can and do enact additional consumer protection laws that may provide stronger or more specific protections.
Q: How do I know which government agency to contact about a specific consumer issue?
A: Start by identifying whether the issue is related to a specific industry (e.g., banking, telecommunications) and whether it’s a local, state, or national concern. You can then research which agency oversees that particular area or contact your state’s consumer protection office for guidance.
Q: Are online purchases protected by the same consumer laws as in-store purchases?
A: Generally, yes. However, there may be additional protections or considerations for online purchases, particularly regarding data privacy and security.
Q: How often are consumer protection laws updated?
A: Consumer protection laws are continuously reviewed and updated as new issues arise. Federal and state legislatures can pass new laws at any time, and regulatory agencies regularly issue new rules and guidelines.
About the Author

Sarah Klein, JD, is a former consumer rights attorney who spent years helping clients with issues like unfair billing, product disputes, and debt collection practices. At All About Lawyer, she simplifies consumer protection laws so readers can defend their rights and resolve problems with confidence.
Read more about Sarah
